Guarding Against Meningococcal Disease: A Comprehensive Guide to Meningococcal Vaccination
Explore the world of meningococcal vaccines in this informative guide. Discover their importance, dosing schedules, and travel considerations. Learn how to protect yourself and your community
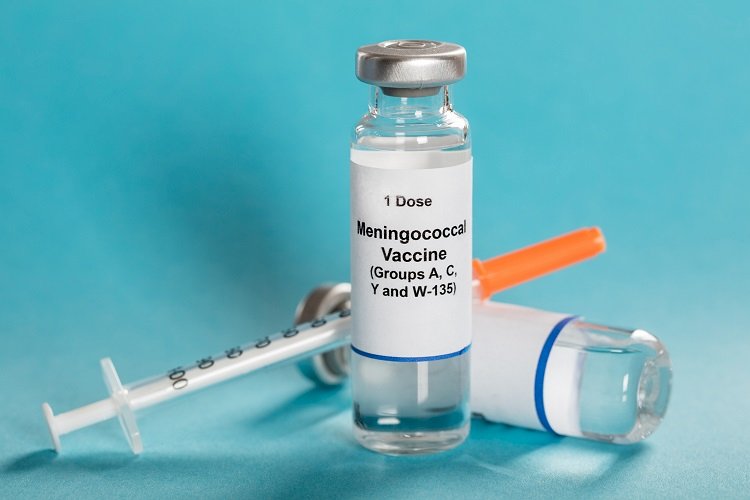
Meningococcal disease, often shrouded in mystery, is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that primarily affects the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. To grasp the significance of meningococcal vaccination, it's essential to comprehend the disease itself.
What is Meningococcal Disease?
Meningococcal disease is caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis, which can lead to severe infections in various parts of the body. The most common manifestation of this disease is meningitis, an inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. However, it can also cause bloodstream infections (septicemia) and other localized infections.
How Does Meningococcal Disease Spread?
Understanding the mode of transmission is crucial. Meningococcal bacteria are typically spread through respiratory droplets from coughing, sneezing, or close contact with an infected person. Crowded living conditions, such as college dormitories or military barracks, can facilitate its transmission.
Symptoms of Meningococcal Disease
Recognizing the symptoms is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs and symptoms include high fever, severe headache, neck stiffness, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, and a characteristic skin rash. These symptoms can escalate rapidly, leading to life-threatening complications.
Populations at Risk
Certain groups are more susceptible to meningococcal disease, including:
- Adolescents and young adults
- Infants
- People with compromised immune systems
- Travelers to regions with high disease prevalence
- Close contacts of someone with a meningococcal infection
What is the Meningococcal Vaccine?
The meningococcal vaccine is a potent shield against the menace of meningococcal disease. In this section, we'll unveil what the meningococcal vaccine is and how it operates to fortify our immune systems against this potentially deadly infection.
Understanding the Meningococcal Vaccine
The meningococcal vaccine is a preventive measure designed to stimulate our body's immune response, preparing it to fend off the Neisseria meningitidis bacterium, responsible for meningococcal disease. It accomplishes this through the introduction of harmless components of the bacterium or a weakened form of the bacterium itself.
Types of Meningococcal Vaccines
There are several types of meningococcal vaccines available, each targeting different strains of the Neisseria meningitidis bacterium. The two primary categories are:
1. Conjugate Vaccines: These vaccines use a small piece of the bacterium (the polysaccharide capsule) attached to a protein. This linkage enhances the immune response, particularly in infants and young children. Examples include MenACWY and MenB vaccines.
2. Polysaccharide Vaccines: These vaccines contain pieces of the bacterium's outer covering (polysaccharides). While effective in adults, they may not be as robust in stimulating an immune response in infants and young children.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
Understanding who should receive the meningococcal vaccine is crucial for effective disease prevention. In this section, we'll explore the target demographics for meningococcal vaccinations.
Target Demographics for Meningococcal Vaccinations
Meningococcal vaccination is recommended for specific age groups and individuals at increased risk of contracting or spreading the disease. Here's a breakdown of who should consider getting vaccinated:
1. Adolescents and Young Adults
One of the primary target groups for meningococcal vaccination is adolescents and young adults. This age group, typically between 11 and 18 years old, has a higher risk of meningococcal disease due to social behaviors and close living conditions, such as college dormitories. Vaccination in this age range helps curb outbreaks and protects individuals during a vulnerable period.
2. Infants and Children
Infants and children can also benefit from meningococcal vaccination, although it is less common than other childhood vaccines. Some types of meningococcal vaccines are recommended for infants, particularly those at higher risk due to specific medical conditions.
3. People with Compromised Immune Systems
Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or medications, are more susceptible to infections, including meningococcal disease. Vaccination is strongly recommended for this group to bolster their protection.
4. Travelers to High-Risk Areas
Travelers planning trips to regions or countries with a high prevalence of meningococcal disease should consider vaccination. This precautionary measure safeguards against potential exposure to the bacterium.
5. Close Contacts of Someone with Meningococcal Infection
If you've had close contact with an individual diagnosed with meningococcal disease, particularly within the same household or among intimate contacts, vaccination may be recommended as a preventive measure.
Importance of Vaccination for Herd Immunity
Meningococcal vaccination not only provides individual protection but also contributes to herd immunity. Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of a community becomes immune to a disease, making it less likely to spread. By vaccinating those at risk, we can create a protective barrier that benefits the entire community, including those who cannot receive vaccinations due to medical reasons.
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
To determine if meningococcal vaccination is appropriate for you or your child, it's essential to consult with healthcare providers. They can assess individual risk factors and recommend the most suitable vaccination schedule.
In conclusion, understanding the target demographics for meningococcal vaccinations is a crucial step in safeguarding public health. By following vaccination guidelines and consulting with healthcare professionals, we can collectively work towards reducing the incidence of meningococcal disease and protecting vulnerable populations.
Indian Academy of Pediatrics Recommendations for Meningococcal Vaccine in India
The Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) plays a vital role in shaping vaccination recommendations and guidelines within India. When it comes to the meningococcal vaccine, the IAP provides important insights and guidance for healthcare professionals and the public. Here, we outline the IAP's recommendations regarding the meningococcal vaccine and its recommended dosing schedule for different age groups in India.
Meningococcal Vaccine in India
The IAP recognizes the importance of protecting individuals, especially children, from meningococcal disease. Meningococcal vaccines are designed to achieve this objective by providing immunity against Neisseria meningitidis, the bacterium responsible for the disease.
Types of Meningococcal Vaccines
The IAP acknowledges various meningococcal vaccines, including MenACWY and MenB vaccines, which target specific strains of the bacterium. The choice of vaccine may depend on factors such as age, risk factors, and local epidemiology.
Dosing Schedule for Different Age Groups
Infants and Young Children
For infants and young children, the IAP typically recommends a series of vaccinations to establish and maintain protection against meningococcal disease. The dosing schedule often includes:
- First Dose: Given at the recommended age, usually during infancy.
- Booster Doses: Additional doses may be administered to reinforce immunity and ensure continued protection. The timing of these boosters may vary depending on the specific vaccine used and local guidelines.
Adolescents and Young Adults
Adolescents and young adults are a key target group for meningococcal vaccination due to their increased risk of the disease. The IAP recommends:
- Primary Doses: Adolescents should receive the initial doses of the meningococcal vaccine as recommended by the healthcare provider.
- Booster Doses: Depending on the vaccine type, booster doses may be required to maintain immunity. These are typically administered during the late teenage years or early adulthood.
Special Considerations
Individuals with specific risk factors or medical conditions may require tailored vaccination schedules. The IAP emphasizes the importance of consulting with healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate vaccination strategy for these individuals.
Side Effects and Risks
Before making an informed decision about meningococcal vaccination, it's essential to consider potential side effects and risks associated with these vaccines. Like any medical intervention, meningococcal vaccines may have both benefits and drawbacks. Let's delve into the possible side effects and risks associated with meningococcal vaccination.
Common Side Effects
Meningococcal vaccines are generally safe and well-tolerated. Most individuals who receive them experience little to no side effects. However, in some cases, mild and temporary side effects may occur. These can include:
- Pain or Redness at the Injection Site: It's common to experience mild discomfort, redness, or swelling at the injection site. This usually subsides within a day or two.
- Fever: A low-grade fever is sometimes reported after vaccination. This is your body's natural response to the vaccine and is usually short-lived.
- Fatigue: Some individuals may feel tired or lethargic for a day or two following vaccination.
Rare Side Effects
While rare, there are some more serious side effects that have been associated with meningococcal vaccines. These include:
- Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions are exceptionally rare but can occur. Signs of an allergic reaction may include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, rapid heartbeat, and a rash. If any of these symptoms occur, seek immediate medical attention.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS): In extremely rare cases, some individuals may develop GBS after receiving a meningococcal vaccine. GBS is a neurological disorder that can cause muscle weakness and paralysis. It's important to note that the risk of GBS from vaccination is significantly lower than the risk of GBS from a meningococcal infection.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
When evaluating whether to get vaccinated against meningococcal disease, it's essential to consider the relative risks and benefits. Meningococcal disease itself can lead to severe health complications, including death. The potential risks associated with vaccination are notably lower than the risks posed by the disease.
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
Individuals and parents should consult with healthcare providers to make informed decisions about meningococcal vaccination. Healthcare professionals can assess an individual's specific health history, risk factors, and vaccine eligibility. They can provide guidance on the most suitable vaccine type and discuss any concerns or questions regarding potential side effects.
Meningococcal Vaccine and Travel
When it comes to travel, especially international travel,
considerations regarding meningococcal vaccination are essential for both
travellers leaving India and those entering the country from abroad.
Meningococcal disease is a global concern, and understanding the implications
of vaccination in the context of travel is crucial. Here, we'll explore
important considerations for both groups of travellers.
Travelers Leaving India
Destination-Specific Requirements
Travelers departing from India should be aware of
destination-specific vaccination requirements. Some countries, especially those
in regions with a higher prevalence of meningococcal disease, may have entry or
exit vaccination mandates. It's advisable to check with the embassy or
consulate of the destination country or consult travel health resources for
up-to-date information.
Routine Vaccination Updates
Before embarking on international travel, it's an excellent
opportunity to ensure that routine vaccinations, including meningococcal
vaccines, are up to date. This is especially important if you are traveling to
regions where meningococcal disease is more common.
High-Risk Activities and Destinations
Consider the nature of your travel activities and destinations.
If you plan to participate in crowded events, visit regions with reported
outbreaks, or stay in communal accommodations, the risk of exposure to
meningococcal disease may be higher. In such cases, consulting with a
healthcare provider about the need for meningococcal vaccination is prudent.
Travelers Coming to India from Abroad
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
Travelers entering India from countries with different
epidemiological profiles may have varying levels of risk regarding
meningococcal disease. Consulting with a healthcare provider before travel can
help assess the need for meningococcal vaccination based on the traveller’s
specific itinerary and risk factors.
Immunization Records
Travelers entering India should carry their immunization
records, including documentation of meningococcal vaccination if applicable.
This can be useful in case of medical emergencies or if the need for healthcare
services arises during the trip.
Cultural and Religious Considerations
India's diverse culture and religious practices often involve
communal gatherings and festivals. Travelers should be aware of local customs
and traditions that may increase the risk of exposure to infectious diseases,
including meningococcal disease. Taking preventive measures, such as
vaccination, can be particularly important in such contexts.
Conclusion
Meningococcal vaccination is a critical consideration for
travellers, whether leaving India or entering the country from abroad. Awareness
of destination-specific requirements, routine vaccination updates, high-risk
activities, and cultural factors can help travellers make informed decisions
about meningococcal vaccination. Consulting with healthcare professionals and
staying informed about travel health recommendations are essential steps to
ensure a safe and healthy travel experience.
In conclusion, the meningococcal vaccine plays a pivotal role in safeguarding individuals and communities from a potentially deadly disease. It is a testament to medical advancements and the dedication to public health. Remember, getting vaccinated is a responsible and noble act that contributes to a healthier world.

































Comments (0)