PUMPING BREAST MILK: A NECESSITY FOR WORKING MOTHERS OR JUST AN EXCUSE?
Want to know why women need to pump and how important it is to breastfeed? Our guide covers the importance of pumping breast milk.

- Introduction
- Importance of breastfeeding
- The challenge for working mothers
- The Need for Pumping Breast Milk
- Balancing work and breastfeeding
- Benefits of pumping
- Pros of Pumping Breast Milk
- Convenience and flexibility
- Involving other caregivers
- Managing milk supply
- Cons of Pumping Breast Milk
- Time-consuming and tiring
- Potential decrease in milk supply
- Challenges of storage and handling
- World Breastfeeding Week and its Significance
- Advocating for breastfeeding
- Promoting awareness
- Balancing Work and Breastfeeding
- Workplace support and policies
- Creating a breastfeeding-friendly environment
- The Emotional Aspect
- Guilt and societal expectations
- Recognizing the choice
- Alternatives to Pumping
- Direct breastfeeding when possible
- Supplementing with formula
- The Impact on the Child
- Bonding with the mother
- Health benefits
- Real-Life Stories
- Personal experiences of working mothers
- Challenges faced and overcome
- How Employers Can Support Pumping Mothers
- Providing dedicated pumping spaces
- Flexible working hours
- Making an Informed Decision
- Considering individual circumstances
- Seeking advice from healthcare professionals
- Conclusion
PUMPING BREAST MILK: A NECESSITY FOR WORKING MOTHERS OR JUST AN EXCUSE?
Introduction:
Breastfeeding is a fundamental aspect of infant care, providing essential nutrients and immune-boosting properties for a child's healthy development. However, for many working mothers, striking a balance between their professional obligations and breastfeeding can be a daunting challenge. This has led to the widespread adoption of pumping breast milk, allowing mothers to provide breast milk for their babies even when they are away. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of pumping breast milk, discussing whether it is truly a necessity for working mothers or sometimes an excuse.
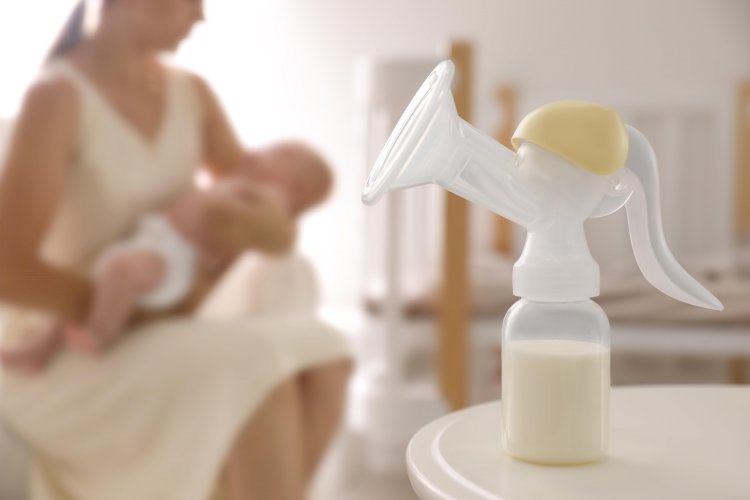
The Need for Pumping Breast Milk:
The demands of modern life often require mothers to return to work soon after giving birth. Pumping breast milk becomes a necessity to ensure that their babies continue to receive the benefits of breast milk even when they are not physically present. It allows them to balance work commitments without compromising their child's nutritional needs.
Pros of Pumping Breast Milk:
a) Convenience and Flexibility: Pumping breast milk provides working mothers with the convenience and flexibility to manage their time effectively. They can express milk at their convenience and feed their babies on schedule.
b) Involving Other Caregivers: Pumping breast milk enables other caregivers, such as partners or family members, to participate in feeding the baby. This promotes bonding and allows mothers some much-needed rest.
c) Managing Milk Supply: Pumping can help mothers regulate their milk supply. It can be particularly helpful when a mother produces an excess of milk or experiences challenges with latching.
Cons of Pumping Breast Milk:
a) Time-Consuming and Tiring: Pumping breast milk can be time-consuming and physically demanding, especially when mothers have busy work schedules. It may lead to additional stress and exhaustion.
b) Potential Decrease in Milk Supply: For some mothers, frequent pumping might signal to the body that less milk is needed, potentially leading to a decrease in milk supply.
c) Challenges of Storage and Handling: Storing and handling pumped breast milk can be challenging, particularly when there are no proper facilities available at the workplace.
World Breastfeeding Week and its Significance:
World Breastfeeding Week is a global initiative aimed at promoting the importance of breastfeeding and advocating for supportive policies for nursing mothers. It raises awareness about the benefits of breastfeeding and encourages communities to support and enable breastfeeding women.
Balancing Work and Breastfeeding:
To ensure successful breastfeeding, workplaces need to implement supportive policies and provide appropriate facilities for nursing mothers. This includes dedicated pumping spaces and flexible working hours to accommodate breastfeeding needs.
The Emotional Aspect:
Mothers often experience feelings of guilt and societal pressure regarding their decision to pump breast milk instead of breastfeeding directly. Recognizing that choosing to pump is a valid choice is essential for maternal well-being.
Alternatives to Pumping:
While pumping is a valuable option for working mothers, direct breastfeeding when possible is encouraged. For situations where breastfeeding or pumping is challenging, supplementing with formula can provide the necessary nutrition for the baby.
The Impact on the Child:
Breastfeeding fosters a strong bond between mother and child. It also offers numerous health benefits, including a reduced risk of infections and allergies.
Real-Life Stories:
Listening to the experiences of working mothers who have successfully balanced work and breastfeeding can provide valuable insights and inspiration for others facing similar challenges.
How Employers Can Support Pumping Mothers:
Employers play a crucial role in supporting pumping mothers. Providing dedicated pumping spaces, allowing flexible work schedules, and fostering a breastfeeding-friendly environment are some ways to support nursing mothers.
Read more: Empowering Working Mothers: Nurturing Breastfeeding in the Workplace
Making an Informed Decision:
Each mother's situation is unique, and the decision to pump breast milk or breastfeed directly depends on various factors. Seeking advice from healthcare professionals can help mothers make an informed choice.
Conclusion:
Pumping breast milk has become a vital solution for working mothers who wish to continue providing the best nutrition for their babies. While it offers many benefits, it also comes with challenges. Understanding the pros and cons and being supported in the workplace can significantly impact a mother's breastfeeding journey. Ultimately, the decision to pump breast milk or breastfeed directly is a personal choice that should be respected and supported.
REFERENCES
1. World Health Organization (WHO) - Official website: www.who.int WHO provides guidelines and information on breastfeeding, pumping, and its benefits for working mothers.
2. American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) - Official website: www.aap.org The AAP offers resources and recommendations on breastfeeding, pumping, and returning to work for new mothers.
3. La Leche League International - Official website: www.llli.org La Leche League is a non-profit organization that provides information and support for breastfeeding mothers, including pumping.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - Official website: www.cdc.gov The CDC offers resources on breastfeeding, including workplace support and pumping facilities.
5. National Institutes of Health (NIH) - Official website: www.nih.gov NIH provides research articles and studies related to breastfeeding and pumping.
6. Academic Journals and Research Papers - Look for peer-reviewed articles on the topic in reputable scientific journals.

































Comments (0)