Teenage Pregnancy : Facts You Should Know
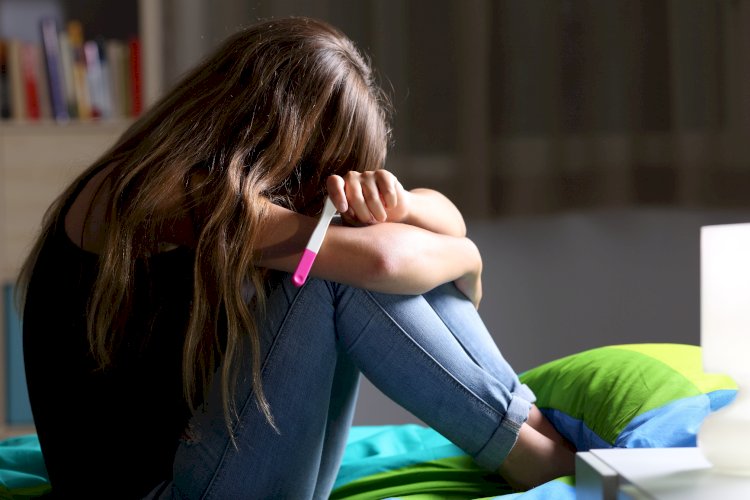

Teenage Pregnancy
Teenage pregnancy is pregnancy in a woman 19 years of age or younger.
At What Age Can a Woman Get Pregnant?
A woman can get pregnant if she has vaginal sex with a man at any age after she has started having regular monthly periods.
Why Is Teenage Pregnancy a Concern?
Concerns for the Mother
Teens are at a higher risk for pregnancy-related high blood pressure (preeclampsia) and its complications, than older mothers. Risk for the baby include premature birth and low birth weight. Preeclampsia can also harm the kidneys or even be fatal for mother or baby.
Pregnant teens also have a higher chance of becoming anemic. Anemia is a reduction in the number of red blood cells. This can make you feel weak and tired and can affect your baby’s development.
Giving birth in the United States is safer than ever, but it is still more dangerous for a teen than for a woman 20 or older. According to Save the Children, each year 50,000 teen mothers around the world die during pregnancy or childbirths.
If you get pregnant as a teen, you might feel frightened and worried about telling your family and friends. Not talking to someone and not getting the help and support you need, can make you feel more isolated and depressed. This can lead to problems in home and at school.
Many pregnant teens drop out of school, and some never complete their education. That means a lot of mothers who get pregnant as teenagers live in poverty. Women who first got pregnant as teens are more likely to have more than one child. A woman with little education and multiple children to care for will find it very difficult to earn a living.
Concerns for Your Baby
A healthy pregnancy lasts 40 weeks. A baby that is delivered before 37 weeks of pregnancy is premature. Teen mothers are more likely to give birth to premature babies. Sometimes, these babies lack complete development in their bodies and brains. Depending on how premature the baby is, this can lead to lifelong difficulties with health and development.
Premature babies also tend to be underweight. Underweight babies might have trouble breathing and feeding as infants. As adults, underweight babies are more susceptible to diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. Low birth weight also affects brain development. A study published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2002 concluded that people who were born underweight had learning problems into adulthood
Infants born to mothers under the age of 20 have a greater risk of dying in their first year compared with babies born to mothers over 20
Concerns for the Father
Fathering a child as a teenager can be a frightening and life-changing event. Teen fathers don’t have to worry about the health implications of pregnancy and childbirth, but they could face similar difficulties staying in school and earning a living.
State laws vary on the legal age for people to have sexual intercourse. Arrest or legal action against teens who are sexually active can have devastating effects. A young man may be required to register as a sex offender if he has reached the legal age (e.g., 18 in some states) and his partner has not (e.g., 17).
What Are the Signs of Pregnancy?
You’ll probably first realize you’re pregnant when you skip a regular period. But if you get a very light period around the time you expect it, don’t assume you’re not pregnant—it is possible to have very light bleeding in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Signs of pregnancy include:
- missed or very light period
- breast tenderness
- nausea, often in the morning
- vomiting
- feeling lightheaded
- fainting
- weight gain
- feeling tired
- swelling abdomen
How Is Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Home Pregnancy Tests
Most supermarkets and drugstores sell home pregnancy tests. These tests are designed to detect pregnancy hormones in your urine. They are most accurate if you use them more than a week after your missed period. If a home pregnancy test indicates you’re not pregnant, wait a week, and take another test to make sure.
If a home test shows you are pregnant, you need to make an appointment with your doctor. He or she will confirm your pregnancy with a blood test and maybe a physical exam.
Your Pregnancy Options
Teens who become pregnant may be afraid to see a doctor, but it is extremely important for the safety of the mother and the unborn child. Your doctor should discuss all options with you regarding your pregnancy, including abortion (ending the pregnancy medically), adoption (giving birth and legally permitting someone else to raise your child), or giving birth and raising the child yourself. Ideally, the future father and family members of both mother and father will be involved in making the best decisions, but this is not always possible. Birth control clinics and public health offices can provide counseling information to help you make the right choices for you and your baby.
Is It Possible for a Teenager to Have a Healthy Baby?
Teen moms can have healthy babies. Make sure you see your doctor as soon as you know you’re pregnant, and attend all your scheduled appointments. Proper obstetrical care throughout your pregnancy is so important to the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. Eat well, exercise, and confide in supportive friends and family members.
Cigarette smoking during pregnancy has been shown to lower birth weight and cause babies to be born prematurely. You should not smoke during pregnancy.
Drugs and alcohol can have very damaging effects on a mother and her unborn child. Do not drink alcohol or use illicit drugs during pregnancy. If you think you might be addicted to drugs or alcohol, ask your doctor about counseling and treatment programs to help you quit.
Only take the medicines your doctor prescribes. Make sure your doctor knows about any over-the-counter medicines you are taking.
It is important for all pregnant women to get proper medical care regardless of how old they are. But because teens’ bodies are still developing, seeing a doctor regularly is especially important for teen mothers.
What to Expect During Doctor Visits
You’ll see a lot of your doctor during your pregnancy. During the first six months, you will probably have an appointment at least once every month. In the last months of your pregnancy, you may see the doctor every other week, ending with weekly visits in your final month. These visits are to make sure you and your baby are healthy.
At the doctor’s office, you will be weighed, your blood pressure will be taken, and your stomach will be measured. As your baby develops, the doctor will feel its position and listen for its heartbeat. Your doctor will ask how you are feeling and if you have any questions. He or she will usually then explain what you can expect during the upcoming weeks of your pregnancy.
It’s a good idea to write down any questions or concerns you have so that you can remember to ask them during your appointment. Make sure you talk to your doctor about your health, the baby’s health, and any emotional or family concerns you have.
See your doctor right away if you have:
- any vaginal bleeding
- severe or continuous headache
- dimness or blurring of vision
- abdominal pain
- persistent vomiting
- chills or fever
- pain or burning during urination
- leaking of fluid from your vagina
- swelling or pain in your legs
Preventing Teenage Pregnancy
The only way to be sure you won’t get pregnant is not to have sexual intercourse. However, there are many methods to reduce your chances of becoming pregnant if you are sexually active.
Prescription Birth Control
Prescription birth control is available through your doctor or a women’s health clinic.
An IUD is a device a doctor implants in your uterus. Hospitalization is not required. The IUD prevents a fertilized egg from attaching to the uterus. It has a 99 percent rate of effectiveness .
Several birth control methods affect hormone levels in your body, so you’re less likely to get pregnant. The most effective is a birth control implant, a very small plastic stick that is inserted under the skin of your arm. Implants stay in place for up to three years. They have a 95 percent rate of effectiveness .
Birth control pills, shots, and patches also affect your hormone levels. They have an effectiveness rate of 91 to 99 .
The diaphragm and cervical cap are devices you place in your vagina when you’re going to have sex. They block sperm from entering your uterus. The effectiveness of these devices is 76 to 85 percent .
Over-the-Counter Birth Control
You can also buy over-the-counter birth control at a drugstore and some supermarkets. These methods are not as effective as prescription birth control, but they do reduce your chance of getting pregnant.
Teen pregnancy rates have been dropping in the United States for at least 20 years. Experts think this is because more sexually active teens use condoms. Proper use of a condom can keep you from getting pregnant. Condoms also protect you from many sexually transmitted diseases when used correctly. The effectiveness of condoms is 76 to 85 percent .
Spermicidal Foam
Sponges treated with spermicide also block sperm from entering your uterus. Used properly, these methods prevent pregnancy with an effectiveness of 75 to 85 percent .
Morning-After Pill
Available in the brands Plan B One-Step, Ela, and Next Choice, this medicine contains hormones that prevent your body from releasing eggs into your uterus and irritate the lining of the uterus to inhibit implantation. Eggs have to come into contact with sperm for you to get pregnant and need to implant in order to start developing properly. The morning-after pill might be a good choice for you if you think your regular birth control didn’t work or you weren’t using birth control. Women 17 and older do not need a prescription for the morning-after pill. The effectiveness of the morning-after pill is 89 percent .
Teen Pregnancy Prevention Programs
According to a study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health in 2008, “Adolescents who received comprehensive sex education had a lower risk of pregnancy than adolescents who received abstinence-only or no sex education” .
Many communities offer counseling and support programs that help prevent teen pregnancy. These groups can provide information on birth control and help teens understand their own sexual limits so they don’t get into situations where they might have unprotected sex and get pregnant. Some programs offer peer counseling, since it might feel more comfortable talking to someone your own age. Contact your health department for information on programs in your area.

































Comments (0)