Thyroid Disorder and Infertility – Is There Any Connection?
What are thyroid disorders and how its dysfunction is related to fertility in both males and women? Check out the complete information and clear your all doubts.

The thyroid gland in a human body is the butterfly-shaped organ in the front of the neck that produces hormones that help in regulating your body’s metabolism and even affects the various vital function of a human body. On the other hand, fertility refers to a couple’s ability to conceive and give birth to a baby. There is a significant connection between thyroid health and fertility, which is sometimes a complex part of conception.
What are thyroid disorders?
Thyroid disorders refer to a group of disorders that cause deregulated functioning of the thyroid gland, resulting in the overproduction (hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid) or underproduction (hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid) of thyroid hormones. Particularly, the thyroid gland releases two types of essential hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).
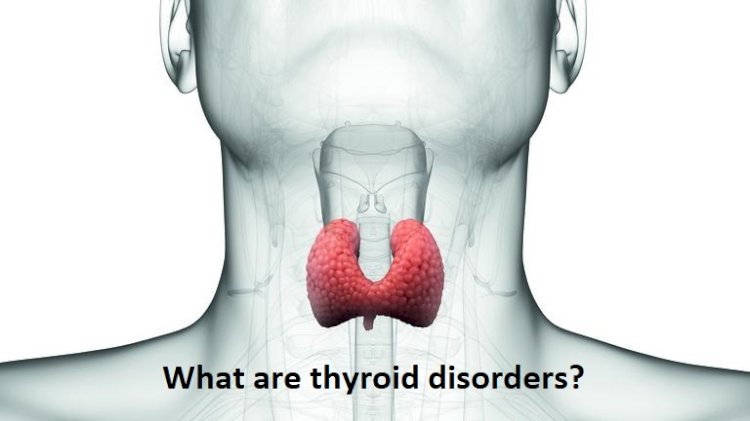
These two essential hormones released by the thyroid gland control metabolism—the way our body utilizes energy and regulates crucial functioning of our body including breathing, heart rate, and body temperature. In a woman’s case, a thyroid gland produces too much or too little of these hormones; this imbalance also can have an effect on her ovaries, making it more complicated to conceive and get pregnant.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism:-
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- Frequent and heavy menstrual cycles
- Fatigue
- Muscle soreness
- Forgetfulness
- Dry skin and hair loss
- Weight gain
- Intolerance to cold
- Depression and insomnia
What’s the role of hyperthyroidism in reproduction?
Too much T3 and T4 in your body can cause:
- Anxiety
- Hand trembling
- Brittle hair
- Increased appetite
- Weight loss
- Irritability/moodiness
- Sensitivity to high temperatures
- Rapid heart rate
- Missed or lighter menstrual periods
How can thyroid disorders affect your fertility?
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can each negatively impact fertility in both men and women, which affects the capability to conceive and become pregnant along with the ability to carry a fetus ahead. The existence of autoimmune antibodies, with or without hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, can also adversely impact your fertility.

Hypothyroidism and Fertility
Fewer releases of thyroid hormone can unfavorably impact fertility in the following ways:
- Disorder of the menstrual cycle, making it difficult to conceive.
- Interference with the release of an egg from the ovaries (ovulation)
- Amplified risk of miscarriage
- Amplified risk of premature birth
Hyperthyroidism and Fertility
The autoimmune condition Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Too much thyroid hormone caused by hyperthyroidism can affect fertility by:
- Disturbing the menstrual cycle
- Causing a decline in sperm count
- Escalating the risk of early-term miscarriage
- Escalating the risk for premature birth
Can thyroid disease cause male infertility?
Infertility is not a female-only concern. Thyroid disorders in men can also negatively affect a couple’s fertility. Studies show that low and more thyroid hormone levels in men can cause: -
- Poor semen quality
- Low sperm count
- Reduced testicular function
- Erectile dysfunction
- Drop-in libido
Diagnosis and Treatment
There are a number of treatments available that can assist to recover thyroid gland function in both men and women. Consult an experienced specialist regarding your medical problem, particularly if the treatment you currently following is not helping your conditions.
Most importantly get your thyroid checked—especially when going for infertility treatments—and finding the correct treatment plan may boost your chance of pregnancy, reduce the miscarriage risk, and improve the health of your baby.
If you are following a healthy lifestyle but still are struggling to conceive, schedule an appointment or contact us today.

 Admin
Admin 































Comments (0)